
Security
Secure Air Distribution
To purify the space and maintain a high level of air quality
In the literal sense, sanitation refers to an action of sanitizing, which means making something healthier or ridding a place or environment of elements deemed undesirable… Synonyms for this term include cleaning, disinfecting, purifying, stabilizing, renewing, circulating, and more.
For an HVAC system, the air sanitation function relies on two main principles:
- Air renewal
- Air circulation

In concrete terms, the air circulation rate and the air renewal rate mean the same thing, i.e., the number of times the air volume in a room is completely circulated or renewed over a period of one hour.
The concept of air circulation and renewal rates both provide the same information, which is to know the number of times a volume of air circulates in a room over an hour.
It is an airflow rate expressed in volume per hour (V/h) or in %. The difference between these two principles lies in the process of circulation. With the renewal principle, the air blown into the room is fresh and comes from the outside. This is not the case for the circulation principle, where the air blown into the room can be fresh, recycled, or both at the same time.
τbr V/h = airflow rate (m³.h) / room volume (m³)
τre % = fresh air flow rate (m³.h) / airflow rate (m³.h) X 100
Air quality monitoring depends not only on the renewal rate but especially on the flows and movements of air in a room, strongly influenced by:
- The diffusion of the blown air and its movement in the volume
- The presence of obstacles (dead zones) and the position of air exhausts or intakes
- Thermal effects (hot air/cold air)
- The nature and concentration of pollutants
Air Extraction or Exhaust
Do not underestimate the impact of air extraction on the final result of effective air treatment in buildings. Air intake points must be far enough from the blowers to avoid any short-circuiting with the blown air. Intake grilles are often installed on the ceiling, which, with ceiling blowing, is not the best solution. The best solution in this case is a wall intake at floor level (prevents cold stratification at the floor level).
With a displacement blowing system, the intake should be at the ceiling.
Extractions will be installed where it is important to capture odors or pollutants: on the ceiling in the case of bathrooms, on elevated hoods for kitchens, laboratories, workshops.

Blowing at high speed; Intake at the lower part on the same side.
Correct local sweeping.

Low-speed blowing; Intake at the lower part on the same side.
Risk of dead zone on the opposite side of the diffuser.

High-speed blowing; Intake at the mid-lower part on the same side.
Very good sweeping of the room.
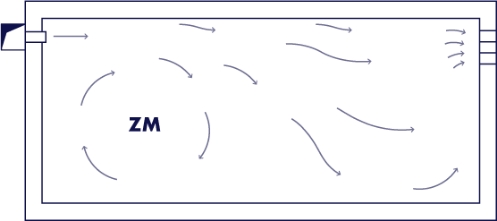
High-speed blowing; Intake at the upper part on the opposite side.
Risk of dead zone on the blowing side.

Low-speed blowing; Intake at the lower part on the opposite side.
Correct sweeping.

High-speed blowing; Intake at the lower part on the opposite side.
Risk of dead zone on the blowing side.
Why is this room ventilated, comfortable, and secure for its occupants and products, and how does the AIRNEO duct by Aéro Textile Concept contribute to this air quality?
The efficiency of air treatment depends on 4 parameters :
- The air renewal in the room results in different cleanliness classes.
- The air diffusion mode leads to a more or less rapid elimination of contaminants.
- Overpressure of the room compared to adjacent rooms.
- Air filtration. The choice of filtration determines the particulate cleanliness of the air blown into the room, retaining particles according to their size.
Putting a room in overpressure naturally protects it against external airborne pollution that would try to infiltrate through openings or orifices and avoids non-ventilated areas (dead zones) by linearly distributing the blown air flow over the entire length of an air diffuser. The advantages of the AIRNEO textile duct are :
- Oriented and linear air diffusion.
- Air diffusion ensuring personnel comfort.
- Movement of the air.
- Air renewal ensured.

Synoptic of a preparation room with air diffusion by a textile duct.
- Controlled atmosphere.
- Confined product zone.
- Homogeneous temperatures.
- Maintenance of optimum conditions.

Numerical simulation of airflows. Control of air vector speeds (m/s) and temperature (°C) of the blown air
